Key pointers:
- What arthritis is and why early management matters
- Common types and symptoms of arthritis
- Non-surgical treatments for pain and stiffness
- Role of physiotherapy, medications, and regenerative options
- When to consider surgery if symptoms persist
What Is Arthritis and Why Does It Cause Joint Pain?
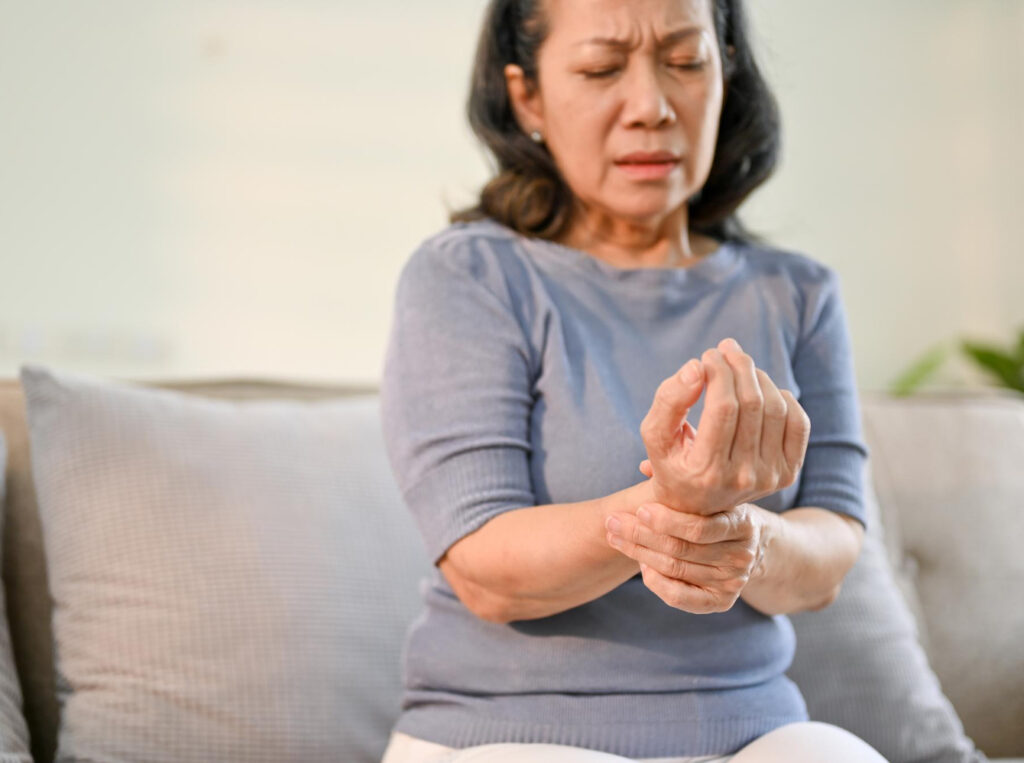
Arthritis is a general term for conditions that affect the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. The most common forms are osteoarthritis, where cartilage wears down over time, and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition that inflames the joint lining.
Over time, the loss of cushioning between bones can make movement painful and limit daily activities. Early recognition and appropriate treatment can help preserve joint function and reduce discomfort.
Can Arthritis Be Managed Without Surgery?
Yes. Many people with mild to moderate arthritis find significant relief through non-surgical treatments. The goal is to reduce inflammation, ease pain, and maintain mobility so daily activities remain manageable.
These conservative options are usually the first step before considering any surgical intervention.
What Are the Common Non-Surgical Treatments for Arthritis?
- Medication for Pain and Inflammation
Doctors may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDs) or pain relievers to control swelling and stiffness. In some cases, topical creams or gels can also help. - Physiotherapy and Exercise Therapy
Targeted exercises strengthen muscles around the joints and improve flexibility. A physiotherapist can design a routine that focuses on joint protection, posture, and gentle mobility. - Joint Injections
For joints that remain painful despite medication, injections such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid may help reduce inflammation and improve movement for a period of time. - Regenerative Medicine (Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy)
PRP therapy uses a small amount of the patient’s own blood, processed to concentrate platelets that support healing in the joint. This option may help reduce pain and promote tissue repair in selected cases. - Lifestyle and Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight, wearing supportive footwear, and avoiding repetitive strain on the joints can reduce pressure and delay disease progression.
When Should You Consider Surgical Options?
Surgery is generally recommended only when non-surgical methods no longer provide relief, or when joint damage severely limits movement. For example, joint replacement may be considered if pain remains constant and interferes with sleep or mobility.
Your orthopaedic specialist will assess imaging results, joint function, and overall health before advising on whether surgery is appropriate.
How Can You Support Joint Health at Home?
Simple daily adjustments can make a difference:
- Apply warm compresses for stiffness and cold packs for swelling.
- Stay active with low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants.
- Use supportive aids, such as walking sticks or braces, when needed.
FAQs
- Can arthritis go away completely without surgery? Arthritis cannot be reversed, but symptoms can be controlled. Non-surgical care focuses on managing pain, preserving mobility, and slowing progression.
- Are joint injections safe for long-term use? Corticosteroid injections can be used occasionally under medical supervision. Your doctor will space treatments appropriately to avoid side effects.
- How effective is physiotherapy for arthritis? Regular physiotherapy improves strength and flexibility, often reducing pain enough to delay or avoid surgery.
- Can PRP therapy help all types of arthritis? PRP may benefit early-stage osteoarthritis or minor cartilage injury, but it is not suitable for every case. Consultation with an orthopaedic specialist is advised.
- When should I see a doctor for joint pain? If pain lasts more than a few weeks, limits daily tasks, or causes swelling and stiffness, seek assessment. Early treatment often leads to better outcomes.
Orthopaedic Care with Dr Sarbjit Singh
At the Centre for Advanced Orthopaedics, Dr Sarbjit Singh provides comprehensive evaluation and management of arthritis using both non-surgical and surgical approaches tailored to each patient’s needs. If joint pain is affecting your mobility or quality of life, an early consultation can help identify options that reduce pain and improve function.